Authors: Lionel Kho, Mindshare, Georges Cheruvelil, Mediaocean, Camila Martins Gerhardinger, TikTok, Eryk Koziol, GroupM
Contributors: Benjamin Rehberg, Teads
Introduction
Author: Lionel Kho, Mindshare
In Southeast Asia (SEA) and India there is an undeniable fundamental shift well underway from multichannel to omnichannel marketing execution, as brands begin to realise tangible value in customer experience. Marketers are tasked with delivering consistent and engaging experiences, from shoppable and quick commerce to in-store interactions. To achieve this they will need to address the challenges of integrated planning, execution, measurement, attribution, and optimisation across a multitude of established and emerging online and offline channels.
In this article, Members of the IAB SEA+India Data, Measurement and Impact Council investigate how marketers are steering through these changes. This is about more than just keeping tabs on how today’s campaigns are performing; it encompasses the courage to try new ways of measuring impact, understanding consumers, as well as maintaining brand cohesion. Navigating through the dynamic regional marketing landscape, the task at hand is both intricate and crucial. Marketers here are grappling with the complex evolution of measurement strategies alongside fragmented regulatory requirements.
To meet the demands of modern marketing, brands must be smarter and more strategic about using their data. Identifying the metrics that matter, unifying data management across first-, second-, and third-party signals, and creating enterprise value by delivering on relevant analytics use cases that make a real difference to the customer purchase journey. This article will explore the many challenges and opportunities in today’s marketing measurement landscape, examining both tactical and strategic considerations to help brands gain an advantage in 2024 and beyond.
The Omnichannel Marketing Landscape
Author: Georges Cheruvelil, Mediaocean
Multichannel and omnichannel are two different approaches to consumer engagement. While multichannel marketing is a strategy that blends the customer experience giving them an opportunity to engage on the channel of preference, it relies on the fact that these brands adapt to working within the boundaries set by the channel.
Multichannel marketing may be more suitable for businesses that want to increase their reach and exposure. On the other hand, omnichannel is a customer-centric sales strategy that intends to provide an experience that is consistent across marketing channels. It enables exposure to the brand and in turn, an opportunity to sell through multiple channels, like desktops, mobile devices, and in-store. Such a strategy may be more suitable for businesses that want to enhance their customer experience and loyalty.
Before choosing between multichannel or omnichannel marketing, business goals, resources, and audience preferences need to be considered since there may also be scenarios where a combination of both strategies may be used. Irrespective of which strategy is chosen by the marketer, an ideal measurement framework needs to exist to enable them to gauge the effectiveness of their ongoing marketing strategies and give them detailed insights to make better decisions of their upcoming marketing activities.
India’s position as the fastest-growing ad spend market in the top 10 globally, alongside SEA’s projected steady growth in ad spend, emphasises the need for multi-channel marketing strategies. Tapping into this potential, however, highlights an exciting challenge: innovating and deploying effective tools to measure, analyse, and attribute Return on Investment (ROI) accurately.
Historically, third-party cookies have been a vital tool for measuring digital ad performance, personalising ads, and optimising ad delivery. However, with the evolving digital ecosystem and shifts in privacy norms, reliance solely on such third-party cookies for measurement is becoming increasingly ineffective. This transition is poised to result in a significant portion of digital advertising going unattributed or misattributed.
In response to these changes, marketers will need to embrace new tools and approaches to adapt their measurement methodologies for a cookieless future. These tools will be pivotal in identifying alternative ways of targeting and engaging users, ensuring that the effectiveness of digital advertising continues in the absence of traditional cookie-based strategies. While the omnichannel approach offers numerous advantages in engaging consumers, it also introduces complex challenges in data privacy, a critical aspect explored in the following section.
From Cookies to Consent: How Marketers Can Adapt to the Evolving Privacy Landscape
Authors: Camila Martins Gerhardinger, TikTok, Eryk Koziol, GroupM
Users’ expectations have increased with greater awareness of how their data is being captured and used, sometimes with unwanted effects, and a desire for greater control over that data. This has long been putting pressure on both regulators and tech providers to address the issue. As a result, we have seen regulations responding to user’s privacy and data controls. Gartner predicts that 75% of the global population will have its personal data covered under modern privacy regulations by 2024. In SEA and India, we have seen Thailand’s PDPA enforced in 2022, Indonesia are set to enforce their privacy bill (PDP) in 2024, Vietnam passed, and enforced, their PDPD this year (2023) and India has just passed (in August 2023) their long awaited Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
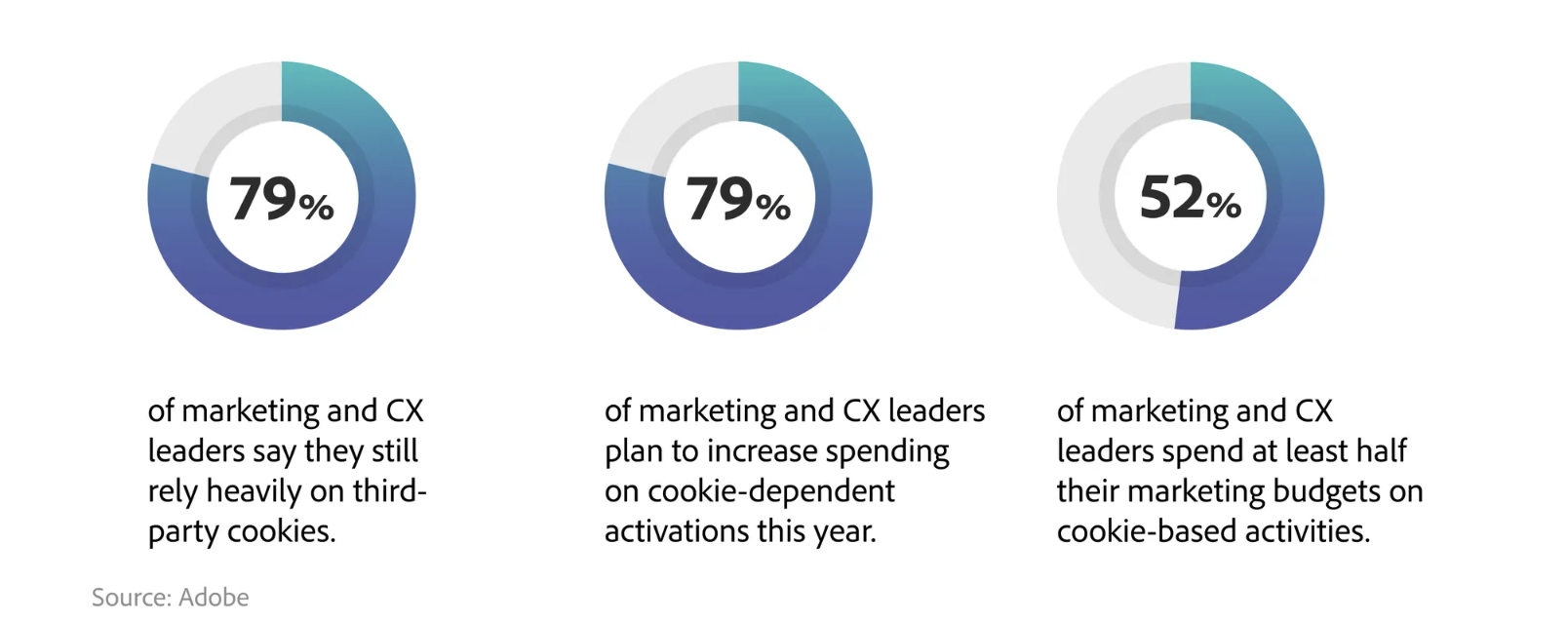 The trend towards decreased reliance on any individual identifier that tracks users across the web and apps space, significantly impacts many use cases which are supported by such technologies today, with 79% of brands surveyed across APAC still heavily relying on third-party cookies. This move away from third-party cookies is a paradigm shift in how the internet works; and it will take a cross-industry approach to ensure it works in the face of increasing user and regulatory needs.
The trend towards decreased reliance on any individual identifier that tracks users across the web and apps space, significantly impacts many use cases which are supported by such technologies today, with 79% of brands surveyed across APAC still heavily relying on third-party cookies. This move away from third-party cookies is a paradigm shift in how the internet works; and it will take a cross-industry approach to ensure it works in the face of increasing user and regulatory needs.
We see impact across the way we collect and build an understanding of our users, how we measure the performance of our efforts to reach and engage with that user base, and finally, how we re-engage or activate those users. A Forrester Consulting study, commissioned by InMobi, found that two out of three organisations in the region have implemented strategic changes to their data, privacy, and marketing practices. Durable solutions are required across all these pillars to ensure the ads-supported business model, which enables an open web providing free content to users, fair compensation to publishers and content providers, and allows advertisers to reach new audiences and existing customers in a meaningful way, continues to thrive.
As we approach the cookieless era, advertisers are dynamically adjusting their measurement strategies to maintain critical insights into campaign performance. In this landscape, the role of data clean rooms (DCRs) is becoming increasingly significant. However, they need to be privacy-compliant to serve as feasible solutions. DCRs are among a range of privacy-compliant tools that are quickly becoming integral to the omnichannel measurement toolkit. They offer a sophisticated way to maintain a balance between effective user engagement and strict adherence to data privacy standards. Alongside DCRs, vendors and partners are actively exploring a variety of privacy-compliant solutions to navigate the challenges of the impending cookieless era.
Bearing all of this in mind, marketers are faced with a seemingly contradictory challenge: how to maintain performance while also addressing key privacy concerns? This is particularly relevant in Southeast Asia and India, where high-growth, scale-up organisations, a significant segment of the regional ads ecosystem, grapple with these complexities.
However, these organisations, typically focused on short-term growth objectives, may overlook the immediate and tangible benefits of engaging with privacy-centric measures. The good news is that performance-minded marketers can successfully measure business growth metrics in a privacy-durable manner. Solid foundations in first-party data enable accuracy, flexibility, and actionability in measurement.
Understanding the evolving privacy regulations and consumer expectations sets the stage for the next discussion: how marketers can strike an effective balance between maintaining brand cohesion and respecting consumer privacy in their omnichannel strategies.
Balancing Brand Cohesion and Consumer Privacy in the Omnichannel Marketing Era
Author: Lionel Kho, Mindshare
Adopting a customer-centric focus in both brand and performance marketing is essential, emphasising a seamless and consistent experience across earned, paid, and owned channels. However, audience resolution in an increasingly disconnected ecosystem is complex. Consumers are more aware of the collection and use of their data and may shift brand loyalties when data collection practices are perceived as invasive. Brands should also prepare for a fragmented tapestry of increased consumer data protection regulation in SEA and India.
How then, can brands continue to provide targeted communications to media audiences, providing engaging consumer experiences across their preferred channels, while continuing to maintain brand cohesion?
Firstly, for any omnichannel strategy to be successful, brands must understand that consumers’ identities are elastic, with changing behaviours and attitudes in the different places and spaces where they choose to give their attention. These elastic identities are how audiences identify with others, and how they form social in-groups and communities. They are fluid and adaptive, driving social trends and cultural norms, and therefore brand affiliations and buyer choices. Brands must find and meet audiences where they are, but equally, have the insight and flexibility to adjust to the context of the communities to which they are speaking.
consumers’ identities are elastic, with changing behaviours and attitudes in the different places and spaces where they choose to give their attention. These elastic identities are how audiences identify with others, and how they form social in-groups and communities. They are fluid and adaptive, driving social trends and cultural norms, and therefore brand affiliations and buyer choices. Brands must find and meet audiences where they are, but equally, have the insight and flexibility to adjust to the context of the communities to which they are speaking.
Source: Mindshare
Secondly, this paradigm shift will force brands to adapt to survive. This invariably includes the need to shift from existing deterministic measurement and attribution techniques towards (perhaps uncomfortably so) probabilistic measurement.
It is worth noting that probabilistic measurement existed well before the dawn of the tracking cookie, and is used broadly by many professions including economists, actuaries, bankers, and so forth. Marketers too must learn to embrace and manage uncertainty if they are to find ways to effectively measure the impact of their campaigns across these diverse omnichannel experiences and be able to attribute ROI meaningfully for cross-channel optimisation.
Importantly, probabilistic measurement is also necessary to embrace AI, which as a media and marketing disruptor is now impossible to overlook. Beyond its creative and dynamic content applications, AI-driven technologies are steadily finding their place in an array of marketing applications, encompassing prediction, personalisation, recommendation, and even fraud detection.
Brands that invested in a strong foundation of first-party data, coupled with a robust tagging infrastructure, will be among the most prepared to leverage their AI readiness, and enhance their attribution and optimisation practices.
Third and optimistically, the environment also presents opportunities for agile brands. The evolution of consumer expectations and new digital spaces means traditional metrics like viewability, reach, and frequency are being re-evaluated.
Lastly, the way in which omni and multi-channel data points can be collected from disparate sources and analysed in a privacy first manner is maturing.
However, do not overlook the relationship between media investment and broader strategic business objectives. It is strategically imperative to use ‘deep funnel’ conversion metrics such as customer acquisition, sales, activation, product engagement and revenue in probabilistic models to better measure the impact of their media spend on executive KPIs beyond impressions, and even attention.
Measurement is both evolving and existential, making it confounding for many and a challenge for most. Disciplined and agile marketers will have robust measurement frameworks in place to understand current campaign performance drivers, and will be open to experimenting with new metrics and attribution methodologies.
Equally, brands must invest strategically in durable first-party data solutions, and have the courage to experiment with innovative, emerging channels and technologies. Brands that can provide a sustained commitment to both will find iterative gains in their ability to measure, attribute and optimise their marketing mix, creating a defensible advantage against their competitors that do not.
Thankfully, there are contemporary tools available which make sophisticated solutions much more accessible to marketers. Whilst the analytics use cases may not be entirely new, the emergence of media and marketing tools that democratise Artificial Intelligence will cause a paradigm shift in the future of marketing.
AI Innovations: Powering the Future of Marketing in a Cookieless World
Authors: Camila Martins Gerhardinger, TikTok, Eryk Koziol, GroupM
To understand how technology can support the cookieless future, this section provides an overview of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its broader application within the industry. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from data, identify patterns, and make intelligent decisions.
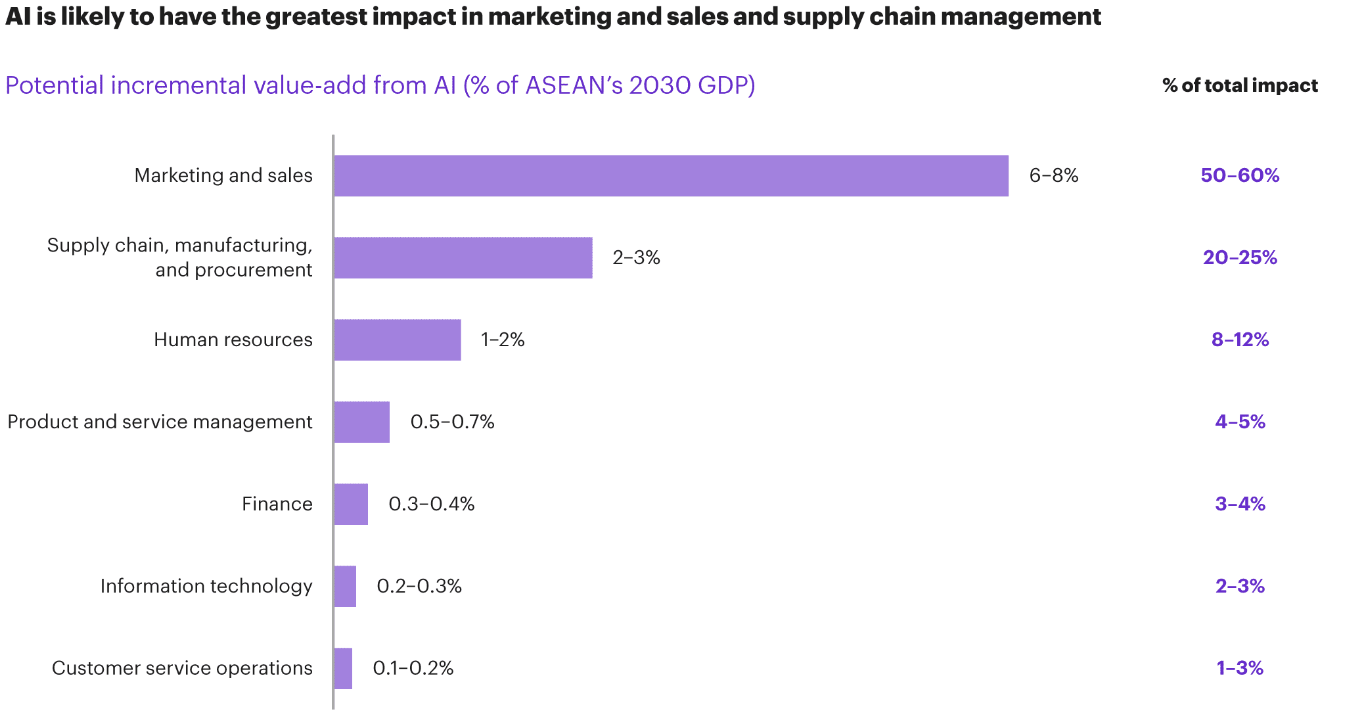 Source: Kearney
Source: Kearney
70% of respondents to a recent Kearney study see AI as crucial to Southeast Asia’s future and that AI adoption needs to be accelerated. The research also reveals that AI can have a strong overall impact: a 10 to 18 percent GDP uplift across Southeast Asia by 2030, equivalent to nearly $1 trillion with the greatest impact being on sales and marketing.
There are numerous sub-streams of AI with Machine Learning (ML) being one of the most common applications within marketing and advertising. Some key ML applications include:
-
Personalisation – This involves analysing customer data to discern behaviours and preferences, aiming to deliver content that resonates more with each user. YouTube enhances accessibility for content creators through its AI-driven multi-language dubbing tool, effectively expanding their audience by adapting to different Asian languages.
-
Predictive Analytics – Predict user behaviours such as purchase intent and churn likelihood. One of India’s largest telecommunications companies Bharti Airtel Limited, commonly known as Airtel, is using ML for customer segmentation, targeted marketing, personalised offerings, churn prediction & retention.
-
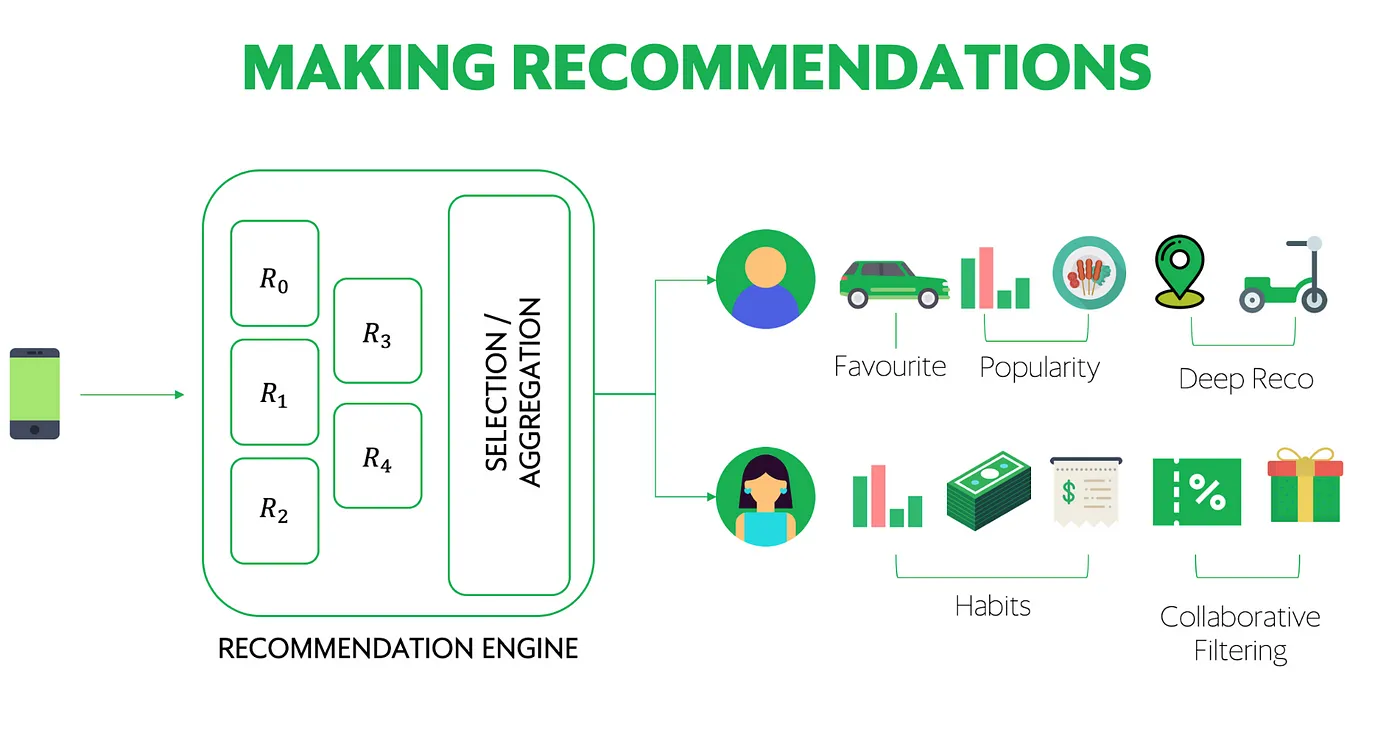
Recommendation engines – Suggesting products, services & content to users based on their web behaviour. Grab, a prominent Southeast Asian super app, leverages AI for its food delivery service GrabFood. This prioritises the user experience by customising restaurant and food item recommendations based on their historical orders and search patterns, along with considerations such as the time of day of the order. This creates a uniquely tailored experience for every individual.
-
Segmentation – Grouping users based on shared characteristics, allowing marketers to tailor campaigns to specific segments. Singapore insurance provider, NTUC Income, unified customer journeys across omnichannel touchpoints, allowing audience segmentation to better understand their prospects across the funnel and to automate the appropriate high value offer to the right segment.
-
Content Analysis – The analysis of content such as images and videos to understand engagement with visual media. Integral Ad Science’s (IAS) Total Media Quality Solution for TikTok solution leverages ML and AI technology to drive accurate and transparent measurement across significant volumes of content.
-
Sentiment Analysis – Processing text-based data social media, reviews and customer feedback to gauge sentiment and brand perception. MediaCorp, Singapore’s national media network, saw its “Ode to BK Rendang” campaign exceed engagement targets by 28.8% and reduce negative sentiment by 3%.
 Source: Meta
Source: Meta
-
A/B Testing & Conversion Rate Optimisation – Automating the split testing process to identify the most effective variations to optimise conversion rates. Porsche Singapore first collected lead information from engaged users which was then processed by Meta’s ML capabilities to identify high-intent users and deliver personalised ads with relevant models.
-
Fraud detection – Detect ad fraud by identifying unusual patterns in click and impression data, protecting ad budgets from wastage. DoubleVerify’s Fraud Lab relies on a variety of approaches to detect fraud, including AI and ML.
-
Conversational Marketing – ML powers chatbots, allowing brands to engage with consumers in real-time and providing personalised assistance. Microsoft’s Azure Open AI service powers Lazada’s LazzieChat to create the first eCommerce AI chatbot of its kind in Southeast Asia. LazzieChat can answer users’ shopping queries on the Lazada platform to provide an engaging, informed and personalised shopping experience.
In addition to the examples above, AI is also being applied in the area of measurement, such as conversion modelling. Unlike traditional measurement approaches that rely on user-level data from a cookie or device, modelled conversions use ML to link user actions where identifiers are not available. This approach can be used to help fill the measurement gaps with data signal loss, and we expect this to evolve further with players such as Google and Meta offering this solution.
AI powered innovative technologies leveraging consented and modelled data, will continue to evolve and drive measurement. Southeast Asian countries are drawing up governance and ethics guidelines for AI, with ASEAN leaders agreeing in February 2023 on the need to develop ASEAN guidelines. To leverage AI meaningfully, brands and agencies may be required to take a privacy-first approach in the application of future technologies as government-led initiatives are announced.
Conclusion
Author: Lionel Kho, Mindshare
The evolving landscape of omnichannel marketing and data privacy in Southeast Asia and India presents a unique and intricate challenge for marketers. As we step into a future where consumer expectations and privacy regulations are continually shifting, it becomes crucial for brands to balance innovative engagement strategies with respectful data practices.
The key to success lies in embracing these changes as opportunities for growth and differentiation. By investing in first-party data, experimenting with new technologies like AI, and adopting privacy-first approaches, brands can create deeply engaging and ethically sound marketing campaigns. Those who navigate these waters with agility and foresight will not only comply with emerging norms but also forge stronger connections with their audiences, ultimately leading the way in the dynamic world of digital marketing.